How to Get an Extremely Accurate EKG/ECG Tracing
The importance of effectively interpreting an EKG/ECG can be a matter of life and death. There are several factors behind receiving an accurate electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG) tracing. The more you apply the following tips, the more likely you are to detect whether a patient’s heart is healthy or not.
1. Properly Prepare Your Patient
Patient preparation is vitally important to the accuracy of your EKG reading. If your patient is not thoroughly cleaned and shaved before applying electrodes to the skin, the EKG reading will compromised. Also, properelectrode placement is one of the key steps in the EKG process.
Follow our complete guide on EKG patient preparation and electrode placement here.
2. Understand Your Waveforms
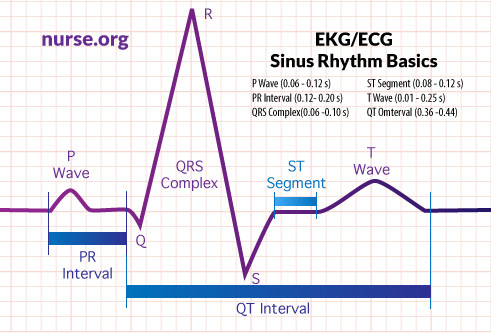
There are various waveform components of the heart that indicate electrical events during each heartbeat. Understanding each one’s purpose and average amplitude, deflection, and duration will help ensure you are able to accurately interpret EKG’s.
- The
P-Wave is the first rising movement of the EKG reading. This movement shows
that the atria are contracting and pumping blood into the ventricles.
- Normal Amplitude: 2 - 3mm high
- Normal Deflection: + in I, II, AVF, V2-V6
- Normal Duration: 0.06 – 0.12 sec
- The
PR Interval displays the transfer time for the electrical signal to move from
the sinus node to the ventricles.
- Normal Duration: 0.012 – 0.20 sec
- The
QRS Complex indicates ventricular depolarization and contraction. It begins
with the minor downward deflection of the Q-Wave.
- Normal Amplitude: 5 - 30 mm high
- Normal Deflection: + in I, II, III, AVL, AVF, V4-V6
- Normal Duration: 0.06 – 0.10 sec
- The
ST Segment traces the early stages of ventricular repolarization. It initiates
at the end of the QRS Complex and continues to the start of the T Wave.
- Normal Duration: 0.08 – 0.12 sec
- The
T-Wave is a small upward waveform which represents ventricular repolarization.
- Normal Amplitude: .5 mm in limb leads
- Normal Deflection: I, II, V3-V6
- Normal Duration: 0.1 – 0.25 sec
- The
QT Interval indicates both depolarization and repolarization ventricular activity.
The QT Interval begins at the start of the QRS complex and ends at the completion
of the T-Wave.
- Normal Duration: 0.36 – 0.44 sec
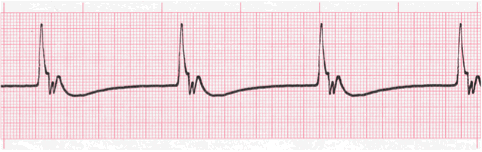
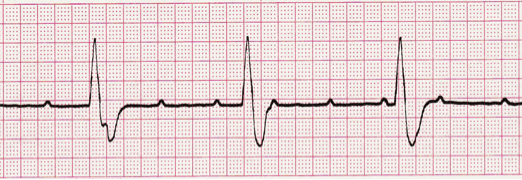
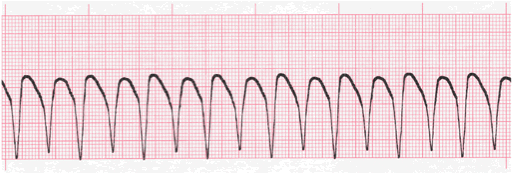
3. Recognize Dangerous Rhythms
When taking an EKG, one must be aware of all the dangerous rhythms that could be indicative of fatal disease. The following are some of the most notable EKG rhythms which lead to negative outcomes:
- Mobitz Type II – AV node becomes entirely refractory to conduction on an intermittent basis.
- Idioventricular Rhythms – presence of atrioventricular dissociation; “slow ventricular tachycardia”
- Third Degree Atrioventricular Block – “Third Degree Heart Block” or “Complete Heart Block”; irregular heart rhythm resulting from a fault in the cardiac conduction system in which there is no conduction through the atrioventricular node, causing a complete dissociation of the atria and ventricles
- Ventricular Tachycardia – abnormal electrical signals in the lower chambers of the heart; 100 or more beats a minute, out of sync with the upper chambers
There are several other types of arrhythmias, or irregular heart rhythms, that you should be aware of to ensure that you are accurately interpreting each EKG.
4. Familiarize Yourself With the Machine
Another important aspect of getting an accurate EKG reading is ensuring that you are using the EKG machine properly. Whether you are using one EKG machine or you are working in a larger hospital where you’re exposed to various machines, you need to familiarize yourself with each system.
EKG machines have different shapes and sizes with a multitude of features, and they are continuing to change. Therefore, you must be up-to-date with all the latest technological advances to ensure you are using each machine properly.
5. Practice Makes Perfect
As with anything, practice makes perfect. If you are an active cardiologist or have aspirations of being one, we highly suggest taking EKG readings regularly and studying the different waveforms. You can never be too familiar with your profession.
There are practice EKG drills, quizzes, and reference guides available for you to take advantage of. So, study up!
Sources:
https://ekg.academy/ekg-waveform-lesson
https://nurse.org/articles/how-to-read-an-ECG-or-EKG-electrocardiogram/
https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/reading-ekg
https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg
https://co.grand.co.us/DocumentCenter/View/653/Rhythms-for-ACLS
https://ekg.academy/learn-ekg?courseid=315&seq=7
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/162007-overview
https://ekg.academy/learn-ekg?courseid=316&seq=7
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ventricular-tachycardia/symptoms-causes/syc-20355138
https://ekg.academy/learn-ekg?seq=9&courseid=315
Recent Posts
-
A New Look at PAD: September is Peripheral Artery Disease Awareness Month
A New Look at PAD: September is Peripheral Artery Disease Awareness Month It's that time of year aga …Sep 3rd 2025 -
Service & Repair
We offer a wide range of service and repair options: standard on-site repair, depot repair (mail-in) …Mar 3rd 2025 -
Love Your Heart: February is American Heart Month!
February is American Heart Month, a time dedicated to raising awareness about heart health and encou …Feb 18th 2025